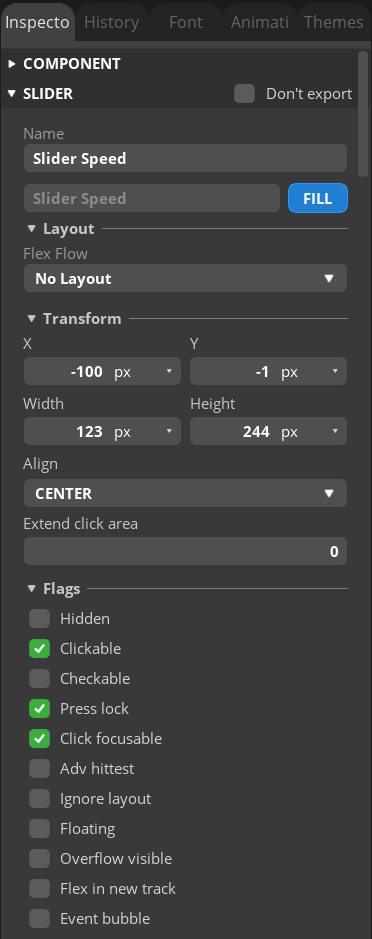
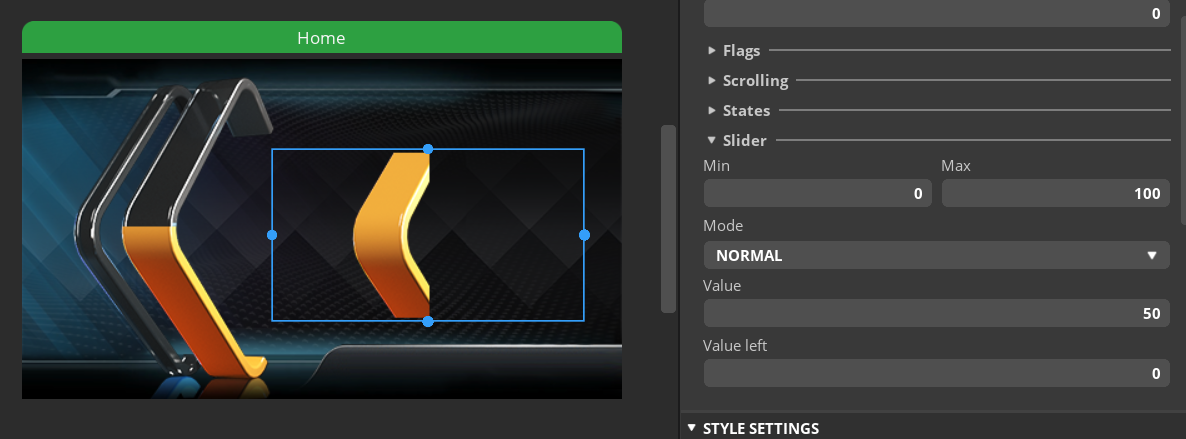
아무생각 없이 export 했다가 sdkconfig보고 기겁을 해서(esp32-s3를 난 설정한적이 없는데!)
부랴부랴 설정이 변경한지 메뉴를 뒤져보니 proejct settings 발견
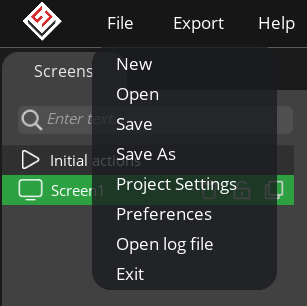
창은 창인데 f4로 안닫히고, esc로도 안닫히는 나쁜 창!
아무튼 board properfies에 esp-s3 이런식으로 되어있었나 보다.

esp32-wroom-32 쓰는 중인데 아마 얘가 esp wrover 칩일꺼라 이거면 될거 같은데
version 1.0.0을 택하면 LVGLdl 8.3.11만 가능해지고

version 2.0.0을 택하면 LVGLdl 9.1.0만 가능해진다.
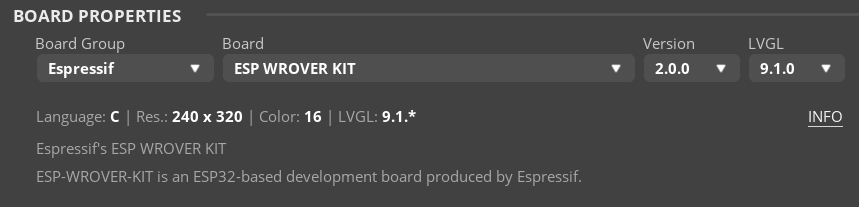
7점대는 완전 구조가 다르다고는 하는데.. 8.3.11이 아니면 약간 낮은 버전에서는 쓰기 힘들려나?
그럼 9.x랑 8.x도 구조가 많이 다른가?
'프로그램 사용 > lvgl' 카테고리의 다른 글
| lvgl textarea (0) | 2026.02.11 |
|---|---|
| squareline studio export (0) | 2026.02.10 |
| lvgl simulator (0) | 2026.02.10 |
| squareline studio / 애니메이션 (0) | 2026.02.03 |
| squareline studio / 화면전환 (0) | 2026.02.03 |