X-CUBE-EEPROM 이 stm32f103 프로젝트에서 안보여서 찾아보는데
어...라... 왜 F만 빠져있냐 =_=
[링크 : https://www.st.com/resource/en/application_note/an4894-how-to-use-eeprom-emulation-on-stm32-mcus-stmicroelectronics.pdf]
[링크 : https://www.st.com/en/embedded-software/x-cube-eeprom.html]
[링크 : https://m.blog.naver.com/chcbaram/223153496808] << STM32G
| STM32C0 series, STM32G0 series, STM32G4 series, STM32H5 series, STM32L4 series, STM32L4+ series, STM32L5 series, STM32U0 series, STM32U3 series, STM32U5 series, STM32WB series, STM32WL series Reference documents EEPROM emulation solutions and application notes are available for other STM32 series as listed below. [1] Application note STM32F0 series EEPROM emulation in STM32F0xx microcontrollers (AN4061) [2] Application note STM32F1 series EEPROM emulation in STM32F10x microcontrollers (AN2594) [3] Application note STM32F2 series EEPROM emulation in STM32F2xx microcontrollers (AN3390) [4] Application note STM32F3 series EEPROM emulation in STM32F30x/STM32F31x STM32F37x/STM32F38x microcontrollers (AN4056) [5] Application note STM32F4 series EEPROM emulation in STM32F40x/STM32F41x microcontrollers (AN3969) [6] Application note Building wireless applications with STM32WB series microcontrollers (AN5289) [7] Reference manual STM32H563/H573 and STM32H562 Arm®-based 32-bit MCUs (RM0481) 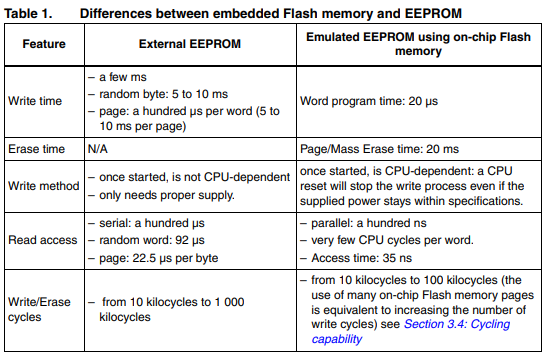 ● eeprom.c: it contains C code for the following project routines: EE_Init() EE_Format() EE_FindValidPage() EE_VerifyPageFullWriteVariable() EE_ReadVariable() EE_PageTransfer() EE_WriteVariable() ● eeprom.h: it contains the routine prototypes and some declarations |
가입 후 아래 링크에서 다운로드 받아야 사용할 수 있나 보다.
대충 봐서는 2개의 섹터를 오가면서 write 하는 듯. wear leveling 등은 구현이 안되어 있을 것 같네
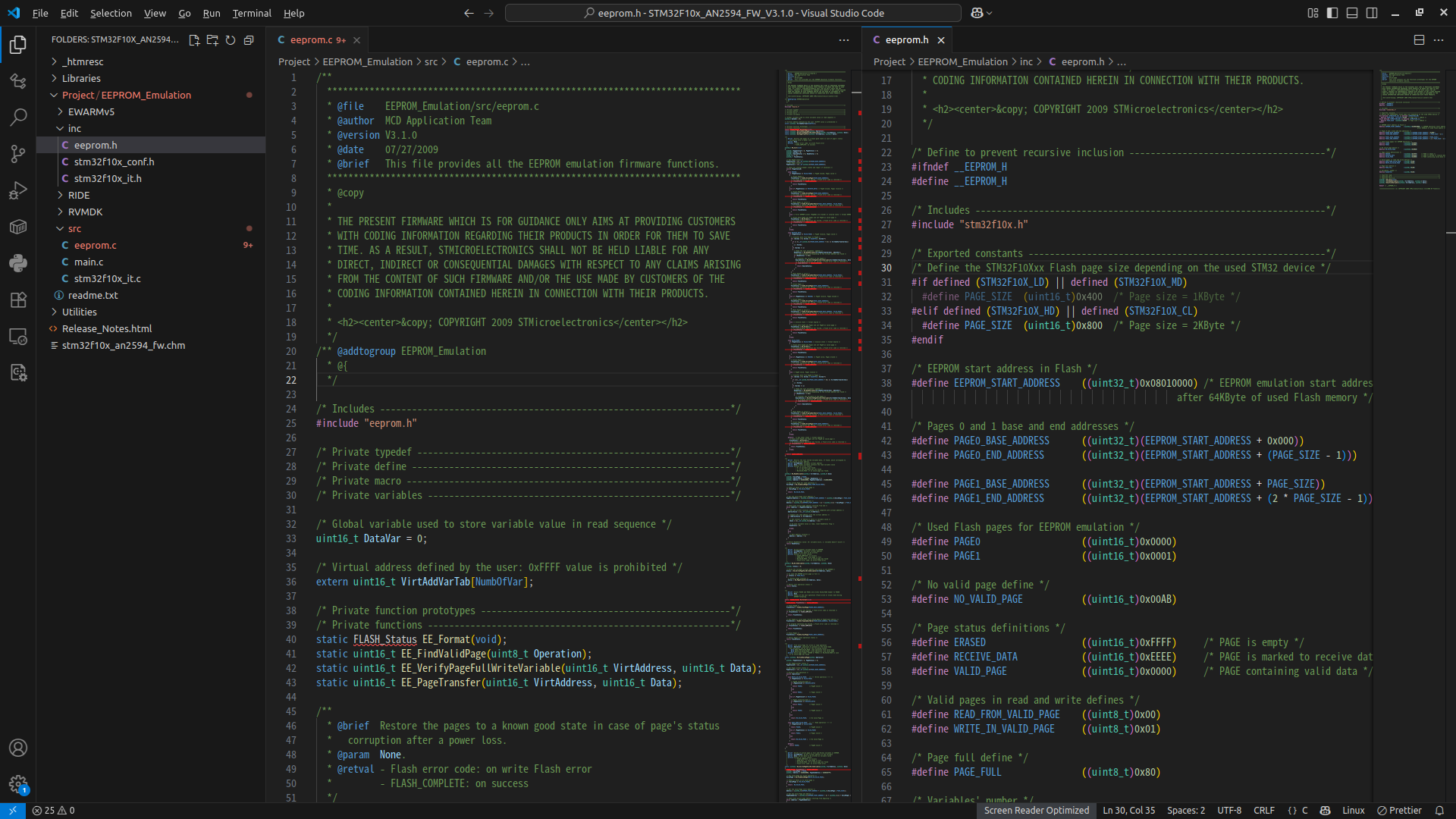
[링크 : https://www.st.com/en/embedded-software/stsw-stm32010.html]
'embeded > Cortex-M3 STM' 카테고리의 다른 글
| EEPROM emulation for stm32 (0) | 2025.10.16 |
|---|---|
| stm32 cpp (0) | 2025.08.08 |
| stm32f103ret flash program / erase 테스트 (0) | 2025.07.28 |
| HAL_FLASH_Program (0) | 2025.07.21 |
| stm32cubeide build analyzer (0) | 2025.07.21 |