'Programming > javascript & HTML' 카테고리의 다른 글
| js split() (0) | 2024.04.12 |
|---|---|
| 자바스크립트 옵셔널 체이닝(optional chaining) (0) | 2024.04.08 |
| javascript groupby map (0) | 2024.03.12 |
| javascript 숫자 (0) | 2024.02.07 |
| 마우스로 테이블 열 변경하기 (0) | 2024.02.02 |
| js split() (0) | 2024.04.12 |
|---|---|
| 자바스크립트 옵셔널 체이닝(optional chaining) (0) | 2024.04.08 |
| javascript groupby map (0) | 2024.03.12 |
| javascript 숫자 (0) | 2024.02.07 |
| 마우스로 테이블 열 변경하기 (0) | 2024.02.02 |
조카가 중학생이 되었는데
생일 선물로 미리 퉁치자고 음악앨범 하나 사주니
그래도 어린이날 선물로 내놓으라고 함 -_-
중학생이면 청소년이지!
| 자전거 수리 가르치기? (0) | 2024.04.21 |
|---|---|
| 하루 늦은 벼룩시장 (0) | 2024.04.13 |
| 개 털 밀기! (0) | 2024.03.30 |
| 처갓댁에서 컴백 (0) | 2024.03.24 |
| 집 정리 (0) | 2024.03.18 |
오랫만에 갔더니
운길산 까지도 겨우 도착하고
운길산 가다가 멈춰서 운길산을 찾고 있었으니 있을리가 있나 -_-
| 서울 자전거 (0) | 2024.10.06 |
|---|---|
| 자전거 대행진 취소 (0) | 2024.04.18 |
| 서울 자전거 대행진 신청 (0) | 2024.04.01 |
| 간만에 자전거 (0) | 2024.02.17 |
| 라이트 손..상? (0) | 2023.05.21 |
X3400 L3400 같은 네할렘 기반의 xeon인데
[링크 : https://www.cpu-world.com/CPUs/Xeon/TYPE-Xeon%203400.html]
Single Intel® Xeon® 3400 series processor in an LGA1156 socket
[링크 : https://www.supermicro.com/manuals/motherboard/3420/MNL-1130.pdf]
랭크가 높아지면(Quad Rank) 1333MHz 까지 가능한 메모리가 800MHz 까지 제한된다.
아마도 core 시리즈 초기형의 경우 메모리 컨트롤러 기술이 성숙되지 않아, 최대 클럭이 상당히 제한되었던 듯.
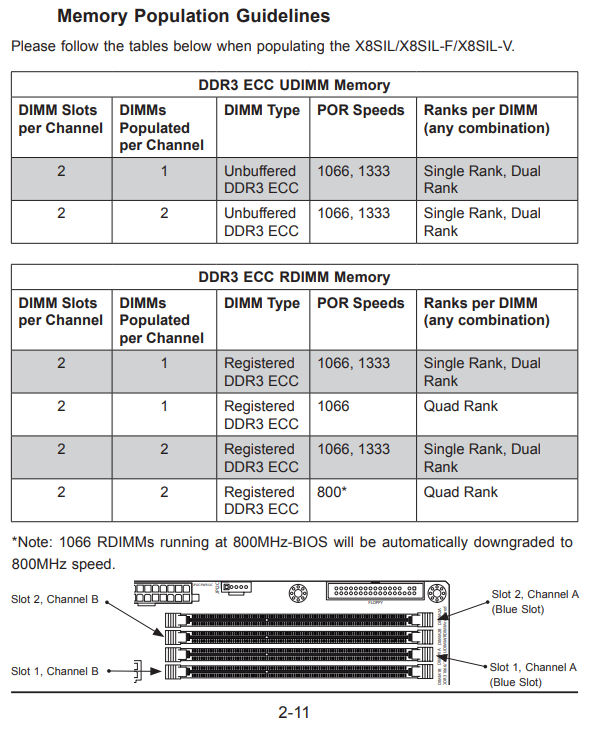
[링크 : https://www.supermicro.com/manuals/motherboard/3420/MNL-1130.pdf]
| xeon phi (0) | 2025.01.03 |
|---|---|
| 보드에 ECC/reg 장착하기 (0) | 2024.04.09 |
| supermicro 구형 IPMI iKVM 접속 (0) | 2024.04.01 |
| xeon에 non-ecc가 가능한가? (0) | 2024.03.31 |
| iKVM 접속 오류 (0) | 2022.11.27 |
pnpm은 또 머냐..
중국어가 써있으니 먼가 쓰기가 꺼려지는건.. 왜 일까!?
[링크 : https://www.npmjs.com/package/qrcode-decoder]
개발자 도구로 봐서는 외부 통신 자체는 안하는 것 같다.
| electron asar 파일 (0) | 2025.08.26 |
|---|---|
| node excel export (0) | 2024.07.18 |
| node.js 웹소켓 채팅 서버 예제 (0) | 2022.07.14 |
| ubuntu 18.04 / nodej.s 18.x 실패 (0) | 2022.05.19 |
| 웹소켓 (0) | 2022.03.25 |
| MSM으로 4disk raid 5 -> 5disk raid 5로 마이그레이션 (0) | 2024.04.15 |
|---|---|
| RAID consistency check fail (0) | 2024.04.09 |
| SMC2108 SSD cachecade (0) | 2024.04.03 |
| raid 케이블이 잘못 연결됨 + LED 깜박이기 (0) | 2024.04.03 |
| MegaCLI (0) | 2024.04.01 |
결국은 fft인가..
[링크 : https://medialink.tistory.com/m/89]
[링크 : https://scribblinganything.tistory.com/249]
[링크 : https://gist.github.com/endolith/246092]
+
https://m.blog.naver.com/dejc2000/221541137592
| 싱크 인터페이스, 소스 인터페이스 (0) | 2024.07.11 |
|---|---|
| shunt(션트) 저항 (0) | 2024.07.11 |
| 아날로그 컴퓨터 (0) | 2023.10.11 |
| rc 시정수 계산 (0) | 2023.10.05 |
| dB(데시벨-상대값)과 dBm(절대값) (0) | 2023.08.23 |
| The CacheCade 2.0 is now supported. Please make sure to use the firmware of version 2.120.53-1235 or later. Older firmware does not support the CacheCade. For the latest firmware, please go to: https://www.supermicro.com/wdl/driver/SAS/LSI/2108/Firmware/.
It also require to purchase CacheCade lincense, AOC-CHCD-PRO2-ESW.
Date Posted 02/18/11 |
[링크 : https://www.supermicro.com/support/faqs/faq.cfm?faq=11360]
| RAID consistency check fail (0) | 2024.04.09 |
|---|---|
| smc2108 (0) | 2024.04.03 |
| raid 케이블이 잘못 연결됨 + LED 깜박이기 (0) | 2024.04.03 |
| MegaCLI (0) | 2024.04.01 |
| MegaRAID Storage Manager(MSM) 설치완료 (0) | 2024.04.01 |
1. LED 깜박이기
어떤 분이 댓글로 Start Locating Drive 하면 불이 깜박일거라고 하셨는데 맞았다.
그 와중에 막 누르다 보니 도움말이 뜨는걸 뒤늦게 발견!
Dell은 일정시간 깜박이고 꺼지더니 이런건 좀 아쉽네

2. RAID 장치 번호
케이블을 보다보니 손댄적도 없는데 상단이 뒷번호가 할당되어 있는걸 뒤늦게 발견(!)
운영상의 차이일수도 있겠지만 혹시 모르니 메뉴얼은 찾아봐야 할 듯.
그래서 RAID card에 꽂히는 SAS 케이블을 두개 순서 바꾸어서 해결!
| smc2108 (0) | 2024.04.03 |
|---|---|
| SMC2108 SSD cachecade (0) | 2024.04.03 |
| MegaCLI (0) | 2024.04.01 |
| MegaRAID Storage Manager(MSM) 설치완료 (0) | 2024.04.01 |
| msm (megaraid) 관리 설치 실패 (0) | 2023.11.14 |
귀찮아서 RAID5로 대충 만들었는데 초기화 하는데 계속 에러가 올라와서 보니 한녀석이 완전 망가진듯
Media Error Count가 슝슝슝
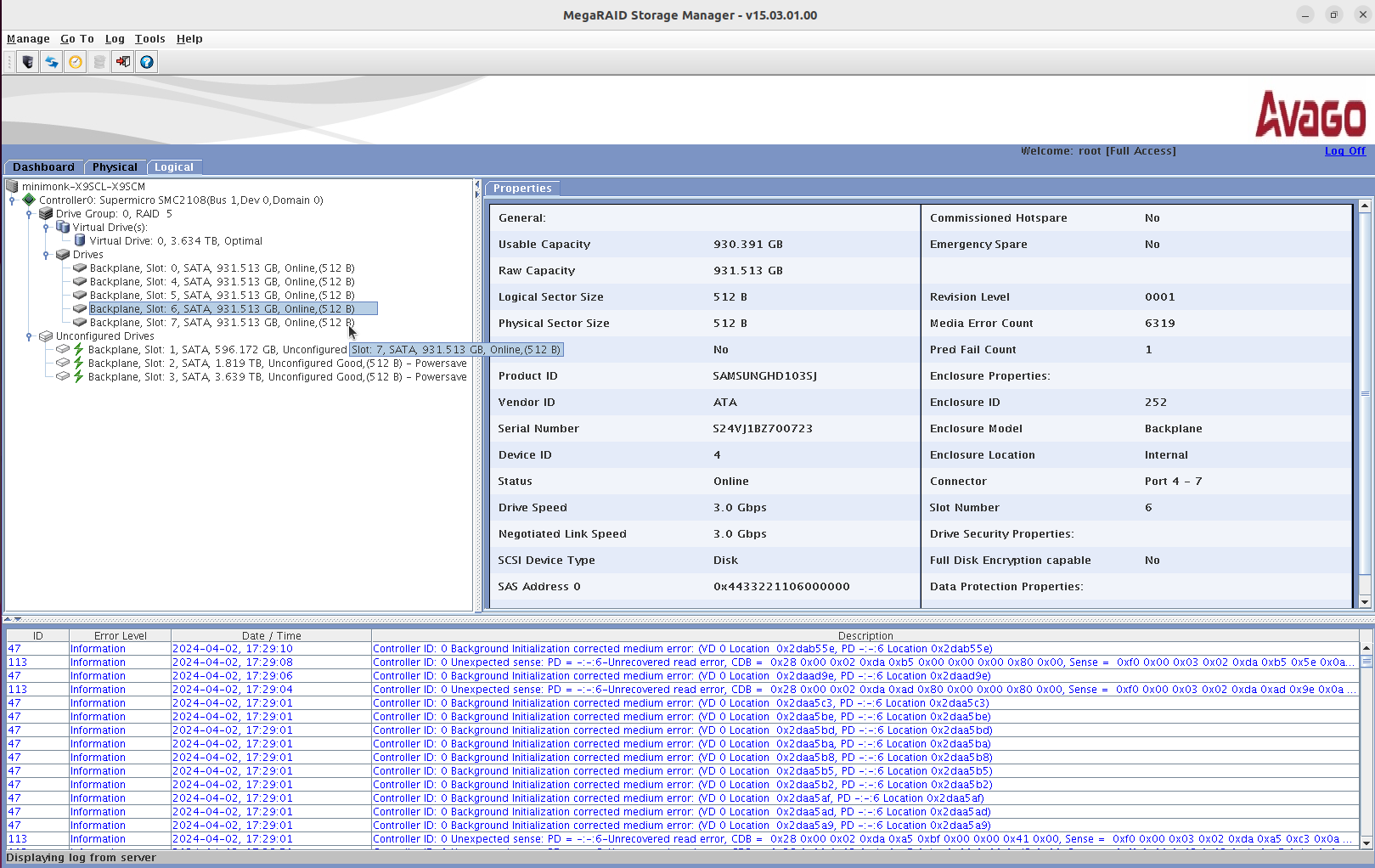
근데...
2x4=8bay 인데
0,1,2,3
4,5,6,7
로 인식이 될 줄 알았는데
4,5,6,7
0,1,2,3
로 상하가 반대로 되었나 slot이 0,4,5,6,7로 뜬다. 메뉴얼 찾아는 봐야할 듯..
| SAS 1TB * 4 구매 (0) | 2024.04.11 |
|---|---|
| 3.5파이 이어폰 잭 저항이... (0) | 2024.04.09 |
| 컴퓨터 셋팅완료 (0) | 2024.03.20 |
| cpu, ram 적출 (0) | 2024.03.19 |
| 다이소 웹캠.. M12 렌즈.. 계륵?! (0) | 2024.03.14 |