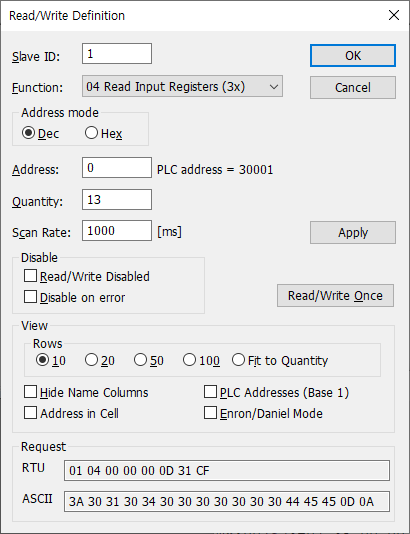
아래 에러들은 SIMD 명령으로 변환하는데 실패한 녀석들인것 같은데
아래와 같은 유형들이 에러로 발생했다.
반복문이 중첩되거나, 반복문 내에서 조건문이 있으면 안되는 것 같고
| tt.c:180:3: note: ===== analyze_loop_nest ===== tt.c:180:3: note: === vect_analyze_loop_form === tt.c:180:3: note: not vectorized: control flow in loop. tt.c:180:3: note: bad loop form. tt.c:61:3: note: ===== analyze_loop_nest ===== tt.c:61:3: note: === vect_analyze_loop_form === tt.c:61:3: note: not vectorized: multiple nested loops. tt.c:61:3: note: bad loop form. |
아래부터는 어떤 에러인지 감이 안오는 녀석들..
지원하지 않는 패턴
| tt.c:83:7: note: Unsupported pattern. tt.c:83:7: note: not vectorized: unsupported use in stmt. tt.c:83:7: note: unexpected pattern. |
지원되지 않는 데이터 타입. 코드를 보니 for문의 비교문에
함수 포인터를 통한 참조(->) 로 보려고 할때는 타입을 추적 못하는 듯?
| tt.c:107:5: note: not vectorized: unsupported data-type tt.c:107:5: note: can't determine vectorization factor. |
no grouped store가 어떤건지 모르겠다.
val = data[];
out = data / 255;
이런식으로 단순화 가능한 코드인데 배열과 포인터로 배열 인자가 선형으로 분석될수 없기 때문에 그런걸지도?
| tt.c:106:3: note: not vectorized: no grouped stores in basic block. tt.c:106:3: note: ===vect_slp_analyze_bb=== tt.c:106:3: note: ===vect_slp_analyze_bb=== tt.c:108:32: note: === vect_analyze_data_refs === tt.c:108:32: note: not vectorized: not enough data-refs in basic block. |
모르겠고..
| tt.c:228:3: note: not vectorized: data ref analysis failed _47 = *_46; tt.c:228:3: note: bad data references. |
모르겠다!!!
| tt.c:238:5: note: not vectorized: not suitable for gather load _47 = *_46; tt.c:238:5: note: bad data references. |
아무튼 AVX로도 변환이 안되는데 .. NEON으로 최적화 될만한 코드는 더더욱 아닐 것 같네.
'프로그램 사용 > gcc' 카테고리의 다른 글
| gcc tree vectorize (0) | 2023.01.26 |
|---|---|
| gcc fstack-protector-strong (0) | 2022.12.06 |
| gcc / 문자열 선언 (0) | 2022.03.17 |
| static link (0) | 2022.02.07 |
| 구조체 타입과 변수명은 구분된다? (0) | 2021.11.18 |